Xanthan gum, a high-molecular-weight polysaccharide produced via the fermentation of glucose by Xanthomonas campestris, is a cornerstone in the formulation of beverages.
Its unique ability to stabilize, suspend, and improve the texture of both dairy and non-dairy drinks makes it indispensable.
This blog delves into the technical mechanisms behind xanthan gum’s role in beverage formulations, supported by scientific data and practical applications.
Rheological Properties of Xanthan Gum in Beverages
Xanthan gum exhibits pseudoplastic (shear-thinning) behavior, a crucial property for beverage applications.
This characteristic allows it to form a thick solution at rest but flow easily when subjected to shear forces, such as stirring or shaking.
When the shear is removed, the viscosity is regained, ensuring a consistent mouthfeel and texture throughout the shelf life.
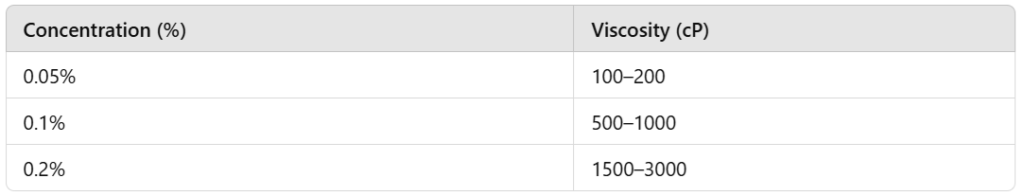
- Viscosity Control: Xanthan gum is highly efficient at very low concentrations (as little as 0.05%–0.2%), imparting viscosity and providing uniform texture across a wide range of beverages. Its shear-thinning properties ensure easy pourability while maintaining the desired thickness when consumed.
- A 0.1% solution of xanthan gum can exhibit viscosities between 500–1000 cP, depending on factors like temperature and pH.
Suspension of Particulates in Beverages
In beverages containing suspended solids (e.g., fruit pulp, proteins, cocoa powder), preventing sedimentation is a critical challenge.
Xanthan gum plays a significant role by creating a viscous matrix that slows down the movement of particulates, keeping them suspended and evenly distributed over time.
- Suspension Mechanism: It interacts with water to form a gel-like network, which increases the viscosity of the liquid and effectively suspends insoluble particles. This property is particularly beneficial for juices, protein shakes, and plant-based beverages like almond or soy milk, where separation can easily occur.
- Stability in Dairy and Non-Dairy Beverages: It can stabilize proteins and fats, preventing phase separation. It can also enhance the suspension of insoluble components, such as cocoa or coffee particles, in ready-to-drink beverages.
- Xanthan gum, at a concentration of 0.05%–0.1% is effective at maintaining particle suspension in beverages with solid content.

Emulsification and Stability in Fat-Based Beverages
In fat-containing beverages (e.g., dairy drinks, plant-based milks), xanthan gum works synergistically with emulsifiers to ensure long-term stability. It helps maintain emulsions by preventing oil droplets from coalescing and separating from the water phase.
- Oil Suspension: It enhances the stability of emulsified systems by thickening the aqueous phase, which reduces the mobility of oil droplets. This is critical in products like flavored milks, plant-based beverages, or drinks containing essential oils.
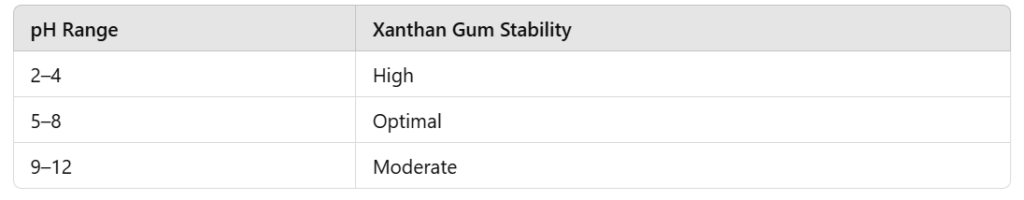
- Temperature and pH Stability: Xanthan gum is stable over a wide range of pH levels (2-12) and temperatures, making it ideal for acidic beverages (e.g., juices) and products that undergo thermal processing, such as pasteurization.
- In fat-based beverages, xanthan gum at concentrations of 0.05%–0.15% maintains emulsified systems for up to 12 months without significant phase separation.

Enhancing Shelf Life and Quality
Xanthan gum significantly extends the shelf life of beverages by maintaining product uniformity, preventing phase separation, and improving resistance to temperature fluctuations.
These attributes are especially valuable in beverages that experience long storage or transportation periods.
- Phase Separation and Sedimentation: Xanthan gum’s ability to stabilize both emulsions and suspensions ensures that the beverage retains its intended composition throughout its shelf life. It helps prevent syneresis (water separation), which is often seen in dairy and protein beverages.
- Microbial Stability: Xanthan gum is resistant to enzymatic degradation and microbial spoilage, contributing to its robustness in beverage formulations. It does not degrade easily, ensuring long-lasting stability in the product.

Conclusion
Xanthan gum is an essential ingredient in beverage formulation, providing suspension, emulsification, and viscosity control to create stable, high-quality products.
Its versatility and effectiveness in a variety of beverages make it indispensable for manufacturers seeking to improve shelf life and ensure consistent product performance.
With its ability to perform across a wide range of pH levels, temperatures, and formulations, xanthan gum continues to be a critical tool in the modern beverage industry.








