Xanthan gum is a polysaccharide widely used in the food industry as a thickening, stabilizing, and emulsifying agent.
The thickening power of xanthan gum is not only a function of its molecular structure but also its interaction with water and other food components.
Let’s explore the underlying science that gives xanthan gum its remarkable thickening capabilities.
Molecular Structure and Formation of Xanthan Gum
Xanthan Gum is produced through the fermentation of glucose or sucrose by the bacterium Xanthomonas campestris.
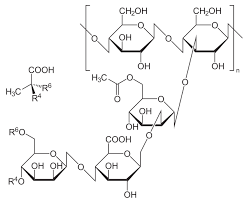
The resulting polysaccharide consists of a cellulose backbone with trisaccharide side chains, typically made up of mannose, glucuronic acid, and acetylated mannose.
This unique structure is crucial for its functional properties, as it imparts rigidity and the ability to form a highly viscous solution at low concentrations.
The rigidity of the xanthan gum structure arises from the ordered helical conformation of its polysaccharide chains.
These helices are stabilized by hydrogen bonding and electrostatic interactions between the carboxyl groups of glucuronic acid and other molecules, giving xanthan gum its distinctive viscosity-enhancing behavior.
Hydration and Solubility
The interaction of xanthan gum with water is central to its thickening ability.
This gum is highly hydrophilic, and hence attracts and binds to water molecules quickly to form a gel-like network.
Even at concentrations as low as 0.1-0.5%, xanthan gum can form solutions with high viscosity, which is especially important for applications requiring minimal ingredient additions.
Also, it does not require any Activation Temperature and can be dissolved in range of -18 to 130 °C.
It exhibits pseudoplasticity—a non-Newtonian behavior where the viscosity decreases with increasing shear rate.
This property is beneficial in the food industry because it allows products like sauces and dressings to pour easily but maintain a thick consistency when at rest.
Interactions with Other Ingredients
Xanthan gum’s thickening power is enhanced by its ability to interact with other ingredients, particularly proteins and other hydrocolloids.
In dairy-based products, it can form a synergistic interaction with casein micelles, contributing to the stabilization and uniform texture of products like yogurt and cream-based sauces.
Moreover, xanthan gum exhibits synergistic effects when combined with other polysaccharides, such as locust bean gum and guar gum.
These combinations can lead to enhanced viscosity and gel strength by forming an entangled network that traps water more effectively.
Thermal and pH Stability
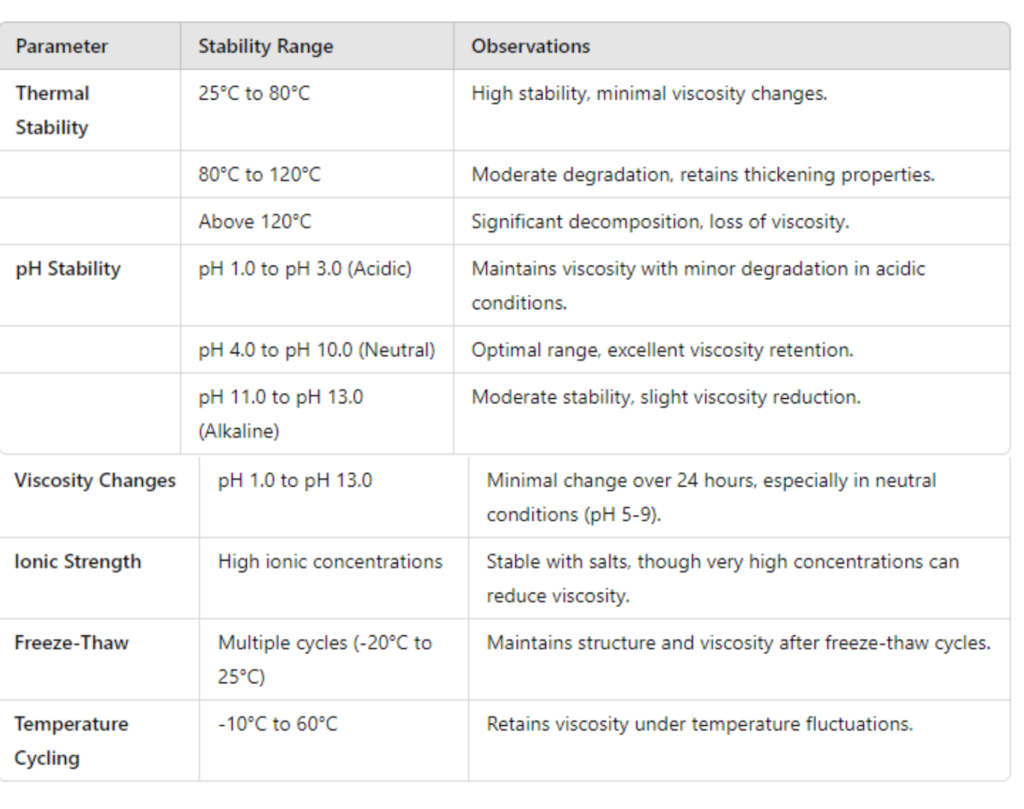
Unlike other thickeners that may degrade or lose their viscosity under heat, xanthan gum retains its thickening properties at elevated temperatures, making it ideal for heat-processed products like soups and sauces. (data in table below).
Its stability across acidic and alkaline conditions makes it suitable for use in products ranging from carbonated soft drinks to vinegar-based dressings.
It’s thermal stability is due to its acetyl and pyruvate groups, which reduce polymer backbone mobility and help maintain viscosity under extreme conditions. Salt or ions further enhance viscosity by shielding electrostatic repulsions between carboxyl groups, stabilizing the structure.
Applications in the Food Industry
Xanthan gum is widely used as a thickener in sauces, dressings, baked goods, and frozen desserts due to its ability to enhance viscosity without altering flavor.
In beverages, it stabilizes particle suspensions, ensuring consistency.
In gluten-free baking, it mimics gluten’s viscoelastic properties, improving texture and making it essential for maintaining dough quality.

Conclusion
Xanthan gum’s thickening power comes from its molecular structure, water-binding capacity, and stability across temperatures and pH levels.
Its ability to improve texture and stabilize emulsions makes it vital in a wide range of food products, from low-fat to gluten-free formulations.








