Tempering chocolate is a precise process that ensures a stable, glossy, and smooth final product.
At the heart of tempering lies cocoa butter crystallization, a key factor that influences the final quality of chocolate.
Understanding how cocoa butter crystallizes and how to control these crystals is essential for creating perfectly tempered chocolate.
Cocoa Butter’s Polymorphic Crystals
Cocoa butter is polymorphic, meaning it can form multiple types of crystals with different properties. These crystal forms, known as Forms I to VI, have distinct melting points and structural characteristics.
- Form I (Gamma): Melts at around 17°C. It is soft and unstable, quickly transitioning to other forms.
- Form II (Alpha): Melts at approximately 21°C. This form is also soft, unstable, and offers a poor texture.
- Form III (Beta-Prime 2): Melts at about 26°C, providing slightly more stability but still not ideal for chocolate.
- Form IV (Beta-Prime 1): Melts at 29°C. It offers a firmer structure but lacks the necessary shine and texture for premium chocolate.
- Form V (Beta): Melts at 34°C. This is the ideal crystal form for tempered chocolate, giving it a shiny finish, a satisfying snap, and a smooth texture.
- Form VI (Stable Beta): Melts at 36°C. It is highly stable but forms over time, contributing to fat bloom in improperly stored chocolate.
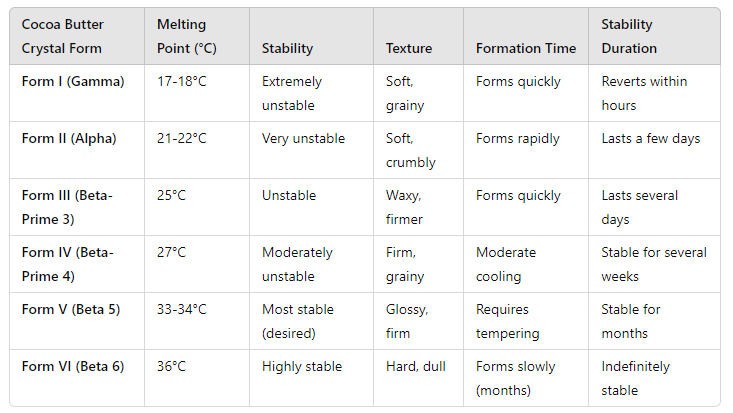
The goal of tempering is to achieve and stabilize Form V (Beta) crystals, as they deliver the ideal properties for high-quality chocolate.
The Tempering Process: Achieving Form V Crystals
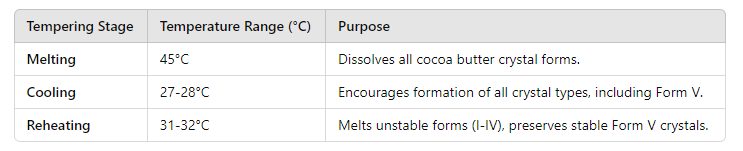
Tempering involves heating, cooling, and reheating chocolate to control the formation of specific cocoa butter crystals, primarily aiming for Form V.
- Melting: The first step is heating the chocolate to around 45°C to dissolve all existing crystal forms.
- Cooling: The chocolate is then cooled to 27-28°C, which encourages the formation of all crystal types, including the desirable Form V and other less stable forms (Forms I-IV).
- Reheating: The chocolate is gently reheated to around 31-32°C, melting the less stable forms (Forms I-IV) while keeping the Form V crystals intact. This selective melting process ensures that only Form V crystals remain in the chocolate.
The precision of these temperature stages is key to successful tempering, resulting in glossy, stable, and well-structured chocolate.
Impact of Crystallization on Texture and Quality
The type of cocoa butter crystals in the chocolate directly affects its texture, appearance, and overall quality.

- Texture: Form V crystals give the chocolate a firm snap, a smooth texture, and a glossy appearance. Forms I-IV result in chocolate that is soft, grainy, or dull in appearance.
- Stability: Properly tempered chocolate resists fat bloom, a whitish discoloration caused by unstable crystal forms (such as Form VI) that can develop over time if the chocolate is not correctly tempered.
- Mouthfeel: Well-tempered chocolate melts at body temperature, providing a luxurious and smooth mouthfeel. The undesirable crystals (Forms I-IV) result in a waxy or greasy texture.
Best Practices for Consistent Tempering

Achieving perfect tempering requires precise control over temperature, as well as handling techniques to ensure Form V crystals dominate the structure.
- Room Conditions: Ambient temperature and humidity should be carefully controlled, ideally around 18-20°C with low humidity, to prevent moisture from affecting the tempering process.
- Seeding Method: The introduction of pre-tempered chocolate, known as seed chocolate, helps initiate the formation of stable Form V crystals. This method simplifies the tempering process and improves consistency.
- Testing Temper: A simple test involves dipping a spoon or knife into the chocolate. If it hardens with a glossy sheen and a sharp snap within a few minutes, the tempering process has been successful.
Conclusion
Cocoa butter crystallization is central to perfecting chocolate tempering, as the formation of stable Form V crystals is what gives high-quality chocolate its shine, texture, and snap.
By mastering the science behind cocoa butter polymorphism and controlling crystallization through tempering, chocolatiers can consistently produce premium chocolate with the desired qualities.








